Summary
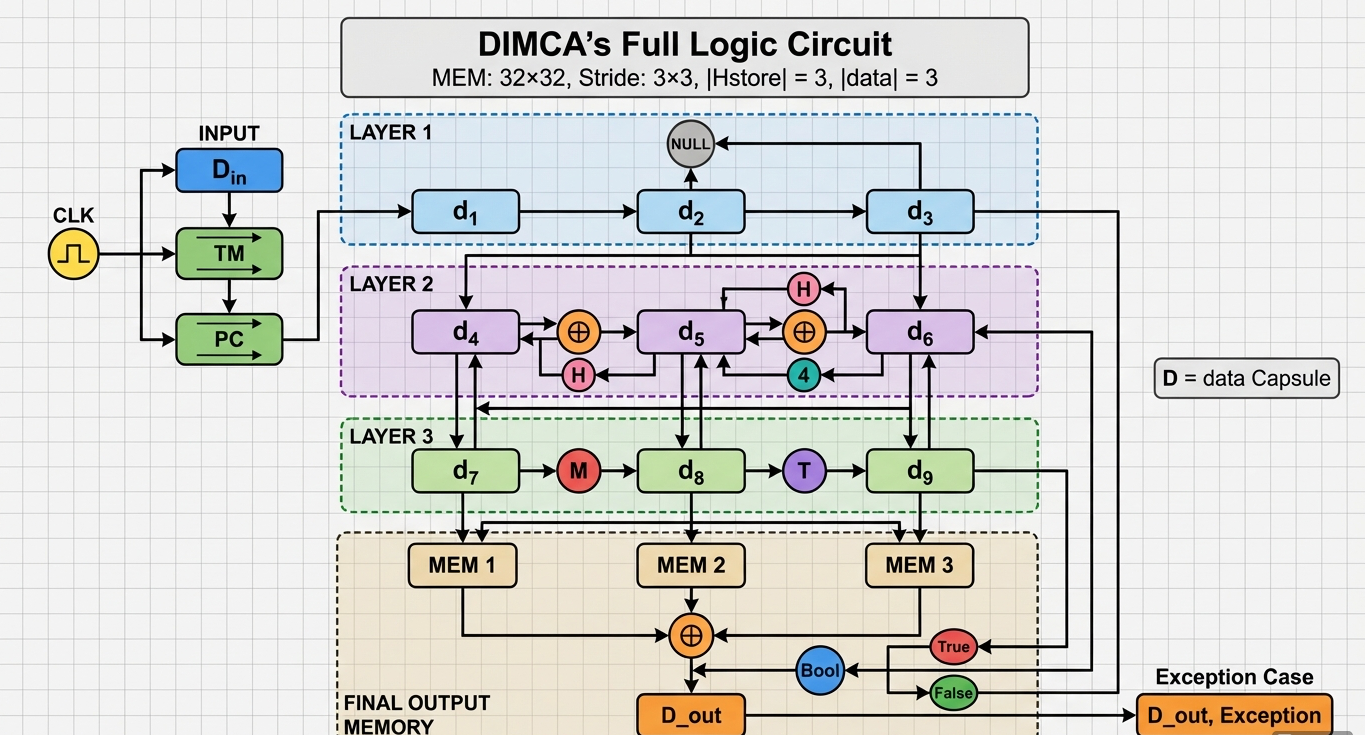
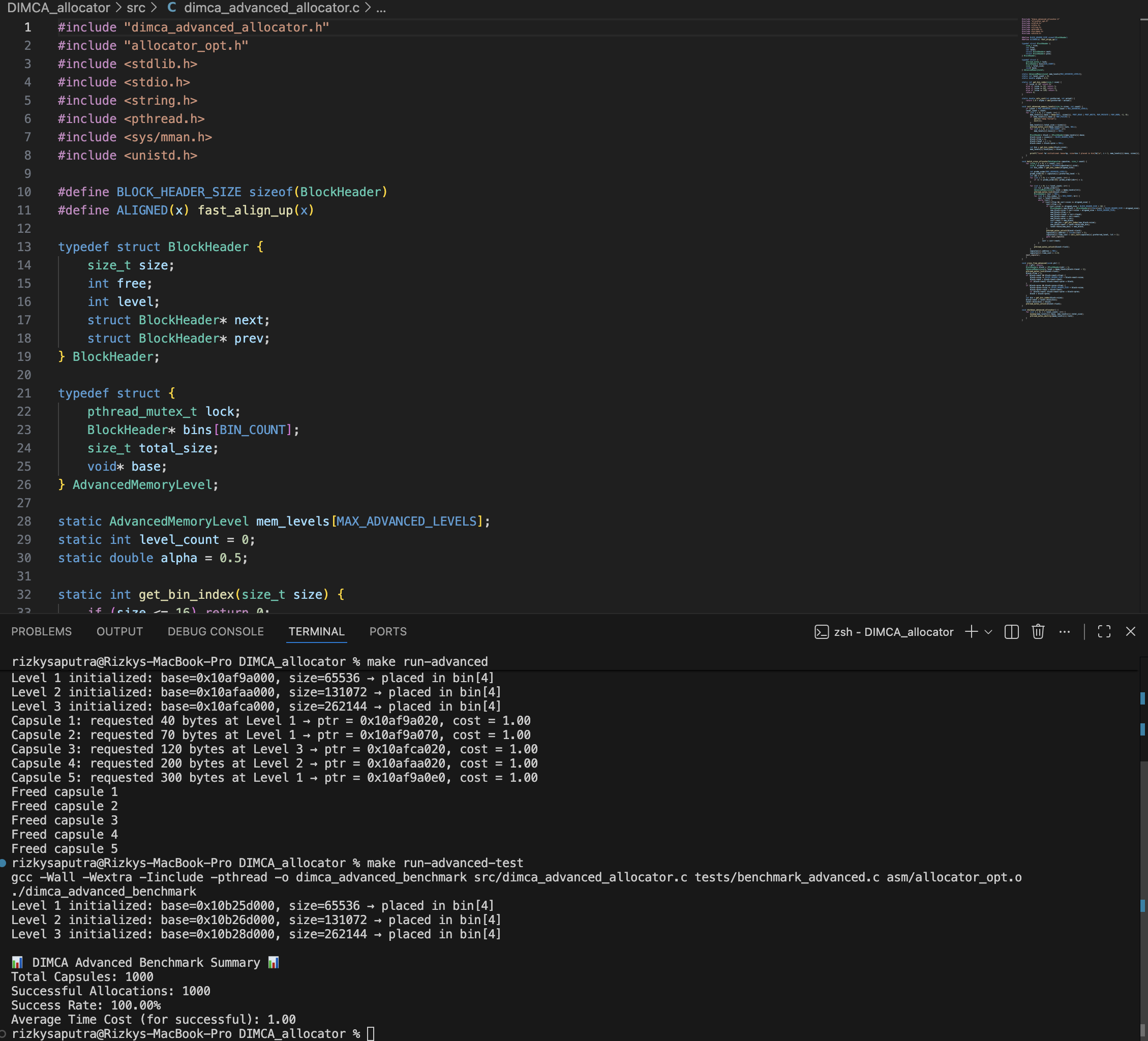
DIMCA (Dynamic Integrated Memory Cross Allocation) is a custom algorithm designed to enhance memory allocation performance by optimizing how data capsules are distributed across multi-level memory pools. The goal is to minimize allocation time penalties due to mismatches between data and memory levels, simulating scenarios found in hierarchical memory systems (e.g., CPU cache levels, RAM tiers, or storage stacks).
Research Purpose
Modern computing systems operate with tiered memory hierarchies:
- Level 1 (L1): Fastest but smallest (e.g., CPU cache)
- Level 2 (L2): Larger but slower (e.g., main memory)
- Level 3 (L3): Largest but slowest (e.g., disk or virtual memory)
Traditional allocation models often place data indiscriminately, causing performance drops due to:
- Time penalties when accessing deeper memory levels
- Lack of alignment between data’s urgency or criticality and memory proximity
DIMCA seeks to fix this by introducing an adaptive and dynamic placement model that:
- Matches data capsule priority levels to memory level tiers
- Penalizes mismatches in levels with a cost function
- Supports concurrent allocation across multiple threads
Future Roadmaps
- LRU-based eviction for full memory levels
- Real-time simulation interface / GUI
- Workload-aware capsule ranking
- Allocation visualization via heatmaps or memory charts
- Domain: Memory System, System Programming, Computer Architecture, Real-Time System
- Core: Multilevel Memory Pooling, Concurrent Allocation, Cache, Virtual Memory
- Neural Networks: Multilevel Memory Pooling, Concurrent Allocation
- Focus: Memory Management, Advanced Algorithms, Smart Allocation System